
We will also include examples to help you understand the process of calculating the cost of goods sold. However, other factors affect the cost of goods sold, for example, the valuation method of inventories, the ending balance, and the beginning balance of inventories. When use properly, however, COGS is a useful calculation for both management and external users to evaluate how well the company is purchasing and selling its inventory. Thus, Shane would sell his June inventory before his January inventory.
Cost of goods sold and small business tax returns
Contents
You will understand the formula and know how to calculate the cost of goods sold during the period for your own company and the principle behind the formula. Assuming that prices rose from January to June, Shane would have paid more for the June inventory and LIFO would increase his costs and decrease his net income relative to FIFO. Specific identification is special in that this is only used by organizations with specifically identifiable inventory. Costs can be directly attributed and are specifically assigned to the specific unit sold. This type of COGS accounting may apply to car manufacturers, real estate developers, and others. IFRS and US GAAP allow different policies for accounting for inventory and cost of goods sold.
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
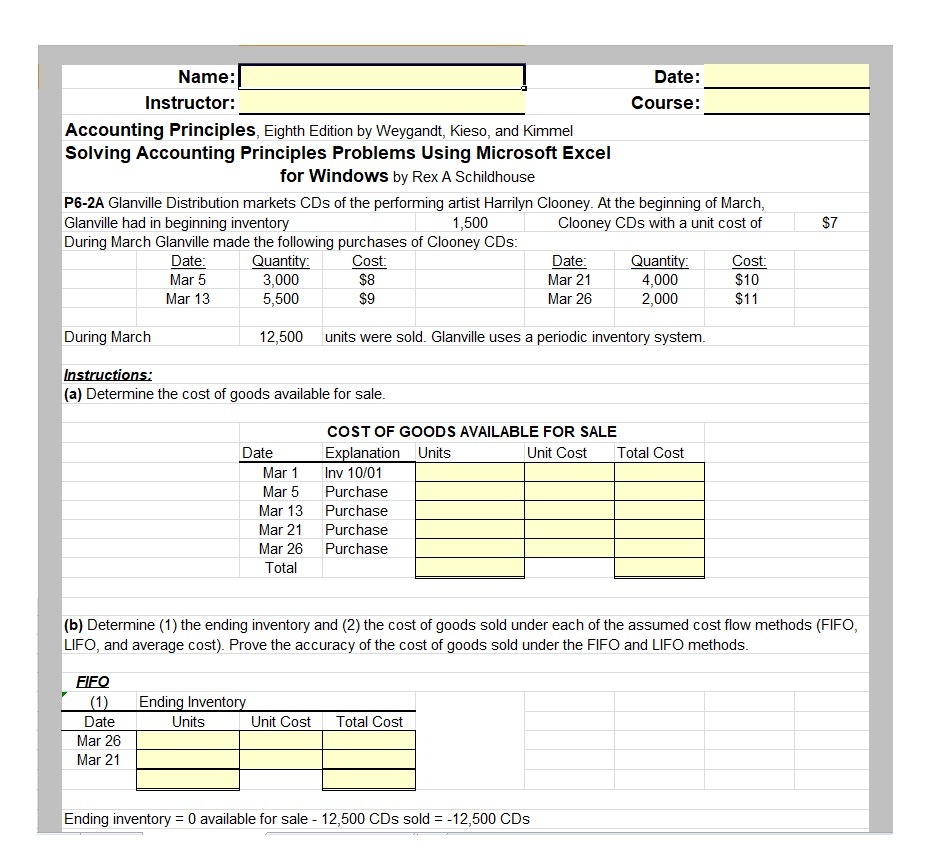
While this movement is beneficial for income tax purposes, the business will have less profit for its shareholders. Businesses thus try to keep their COGS low so that moving expenses net profits will be higher. In this case, Harbour Manufactures uses a periodic inventory management system and FIFO method to determine the cost of ending inventory.
- Shane also can’t prepare and accurate income statement until the end of each quarter.
- As we can see, the cost of goods sold is $200,000, leading to a gross profit of 100,000.
- So, the cost of goods sold is calculated using the most recent purchases whereas the ending inventory is calculated using the cost of the oldest units available.
- So, in the case of service companies, if COGS is not reflected in the income statement, then there can be no COGS deduction.
Cost of Goods Sold Formula (COGS)
For information pertaining to the registration status of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing. Selling and administrative expenses for the year amounted to $110,000. Calculating the cost of goods sold can become a lengthy and tedious process, but the process becomes much simpler when using an online calculator. Now, let’s look at an example of a food delivery services company, Zoot, that picks up parcels from various suppliers and delivers it at the doorstep of the consumer. Investigating alternative suppliers or materials can sometimes lead to cost savings. The above example shows how the cost of goods sold might appear in a physical accounting journal.
Formula:
By contrast, fixed costs such as managerial salaries, rent, and utilities are not included in COGS. Inventory is a particularly important component of COGS, and accounting rules permit several different approaches for how to include it in the calculation. For other business structures, the deduction still applies but might be reported in different forms corresponding to their tax filing requirements.
Operating expenses help establish a budget for each department and evaluate the overhead costs spent by the company. While COGS and operating expenses are different, they are both important in measuring the success of a business. For example, if you are a manufacturing company, you may want to invest in machinery that can automate some of the production processes. Improving your bottom line also means finding ways to automate and streamline processes. Operating expenses are expenses that are indirectly tied to producing the goods or services.
COGS influences key financial indicators ranging from pricing to profit margins and factors into analyses like the breakeven formula directly. COGS and operating expenses are different sets of expenditures incurred by the business in running their day-to-day operations. Here in our example, we assume a gross margin of 80.0%, which we’ll multiply by the revenue amount of $100 million to get $80 million as our gross profit. Generally speaking, COGS will grow alongside revenue because theoretically, the more products and services sold, the more must be spent for production. As another industry-specific example, COGS for SaaS companies could include hosting fees and third-party APIs integrated directly into the selling process.
In this example, Harbour Manufacturers uses the perpetual inventory system and FIFO method to calculate the cost of ending inventory and COGS. It is important to note that under the periodic inventory system, the inventory left at the end of the year (closing inventory) is counted physically. If COGS increases, the net income decreases which means fewer profits for your business. Therefore, it is important for you as a business to keep COGS low in order to earn higher profits.
Calculate COGS by adding the cost of inventory at the beginning of the year to purchases made throughout the year. Then, subtract the cost of inventory remaining at the end of the year. The final number will be the yearly cost of goods sold for your business. The cost of goods sold (COGS) refers to the cost of producing an item or service sold by a company.
